There’s trash within the deepest ocean depths, at some 35,700 toes beneath the floor. There’s additionally trash on Mars.
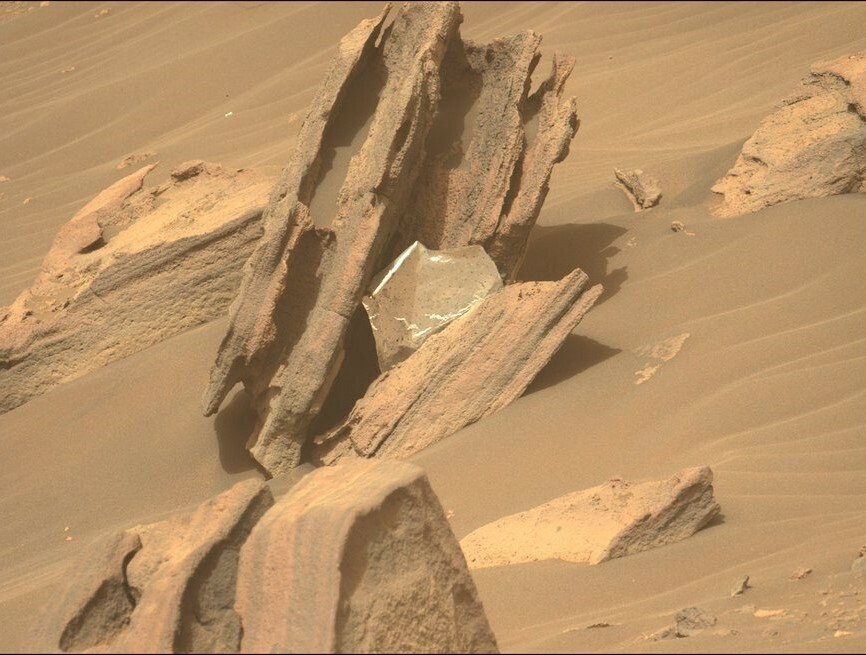
Whereas searching for hints of previous microbial Martian life, NASA’s Perseverance rover lately noticed touchdown particles caught in a jagged rock. It is thermal materials the house company used to guard the Perseverance spacecraft from excessive temperatures because it journeyed to Mars and plummeted by way of the Martian ambiance.
“My crew has noticed one thing sudden: It’s a bit of a thermal blanket that they suppose could have come from my descent stage, the rocket-powered jet pack that set me down on touchdown day again in 2021,” NASA tweeted from the Perseverance rover account on Wednesday.

A looming query is how the foil-like particles discovered its approach to this area in Mars’ Jezero Crater, some two kilometers (1.2 miles) from the place touchdown gear (the “rocket-powered jet pack”) crashed within the Martian desert.
“Did this piece land right here after that, or was it blown right here by the wind?” the house company puzzled.
The Perseverance rover expertly landed on Mars in February 2021. On its manner down, the spacecraft holding the rover ditched quite a lot of devices and objects, together with a warmth defend, a supersonic parachute, and a rocket-powered sky crane that lowered the rover to the bottom. The car-sized robotic has already rumbled by its jettisoned parachute, so it is not terribly shocking the rover now stumbled by extra touchdown particles.
Perseverance would not have a lot time to admire trash. It is now getting into the prime of its mission because it explores a dried-up river delta within the Jezero Crater. Some 3 billion years in the past, NASA’s planetary scientists suspect this space was full of water.
“This delta is likely one of the finest areas on Mars for the rover to search for indicators of previous microscopic life,” NASA mentioned.