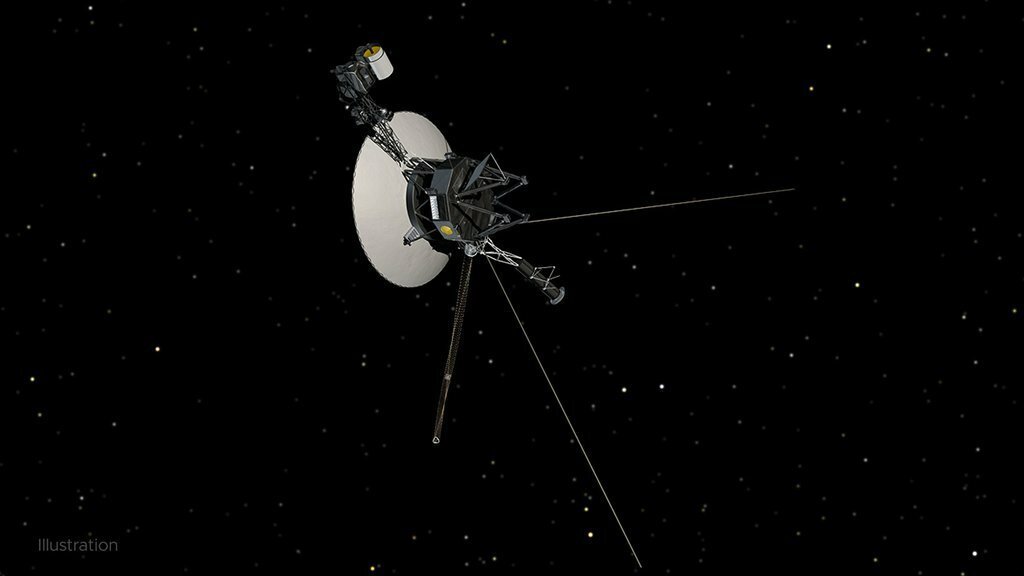
The Voyager 1 spacecraft is sending again some funky information from interstellar area that is leaving NASA engineers scratching their heads.
Readouts on the orientation of the Seventies-era area probe now look like randomly generated or do not replicate any doable situation the spacecraft might be in, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory officers stated this week.
The problematic information are coming from the so-called “perspective articulation and management system,” or AACS, the onboard gear that measures, stories, and adjustments the place of the automobile in area. The system retains an antenna pointed at Earth, which permits it to ship information dwelling.
- It took numerous work to launch humanity’s biggest message into area
- The interstellar dream is dying
- NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft is now flying by means of the celebrities
The brand new weird scenario calls into query the long run for the long-duration mission. On condition that Voyager 1 continues to return information from its science devices, all indicators counsel the controls are nonetheless working, although the info would not make sense, the U.S. area company stated. It in any other case appears to be functioning usually.
“A thriller like that is form of par for the course at this stage of the Voyager mission,” stated Suzanne Dodd, challenge supervisor for Voyager 1 and a couple of in a NASA assertion launched Wednesday.
“A thriller like that is form of par for the course at this stage of the Voyager mission.”
Each Voyager 1 and a couple of are nearly 45 years previous, which is way past their authentic life expectancy. Interstellar area is a high-radiation atmosphere that no spacecraft has ever flown in earlier than, she stated, so surprises are nearly anticipated to come up.
Voyager 1 is 14.5 billion miles from Earth. Meaning gentle takes 20 hours and 33 minutes to journey that distance. In different phrases, the lag between getting a message to Voyager and receiving a response is about two days.
“There are some huge challenges for the engineering staff,” Dodd stated. “However I believe if there is a option to resolve this concern with the [telemetry], our staff will discover it.”

Voyager 1 has been exploring the photo voltaic system since 1977, together with its counterpart, Voyager 2. They had been initially meant to review Jupiter and Saturn, their moons, and Saturn’s rings. For the two-planet mission, they had been constructed to final simply 5 years.
With their preliminary success, engineers doubled the missions’ aims to incorporate two extra large planets, Uranus and Neptune. Between the 2, the spacecraft have explored 4 planets, 48 moons, and a bunch of planetary magnetic fields and rings.
The spacecraft generate about 4 fewer watts of energy yearly, limiting the variety of techniques they’ll function. The mission staff has turned off gear to order energy. No science devices have been powered down but. The aim is to maintain the Voyagers operating past 2025, in line with NASA.
Comply with Mashable SEA on Fb, Twitter, Instagram, YouTube, and Telegram.